Eternal Sunshine: What You Need to Know About Lab Diamonds

Over its centuries-old history, the diamond has established itself as the most expensive and desired stone. Diamond jewelry is girls' dream worldwide, and an engagement ring with a large central diamond has become an international symbol of love.
Despite the high (somewhat even inflated) cost of sparkling stones, the diamond industry, from the inside, looks far from being as clean and flawless as the finished product. However, technology does not stand still.
Relatively recently, less than 70 years ago, scientists managed to "grow" a diamond in the laboratory for the first time. In early 1997, such stones first appeared on the market. Now laboratory diamonds are gaining rapid popularity all over the world.
As a jewelry expert, I am constantly asked what the difference is between a lab-grown diamond and a real one. So, let's take a brief look at the evolution of the diamond industry and the role of lab-grown diamonds in it.
What Are Lab Diamonds?

A lab-grown diamond is a diamond grown in a laboratory under conditions that fully recreate the natural growth environment for diamonds. Grown diamonds are 100% carbon and have the same chemical, physical and optical properties as natural diamonds.
With all the variety of names, laboratory diamonds are real diamonds. They have identical chemical properties and appearance to diamonds mined from the bowels of the Earth. The difference is only the origin, while laboratory diamonds have several undeniable advantages.
What Are the Advantages of Lab Diamonds?

Laboratory diamonds have many advantages over natural stones. Here are the most common:
• Cost: Lab-grown diamonds are 20-30% cheaper than mined diamonds of similar quality.
• Quality: Laboratory diamonds have fewer and smaller inclusions than natural diamonds, making them brighter and more beautiful.
• Eco-friendly: Mining diamonds requires energy and resources, while laboratory diamonds are created in a closed environment.
• Availability: Laboratory diamonds can be produced to any size and cut design, so you can easily find a diamond of the exact size and shape you need.
Laboratory diamonds are a great alternative to natural diamonds that have the same brilliance and quality but are also more affordable and can be purchased in any size or cut. Furthermore, despite its origin, a lab-grown diamond is still a real diamond that can be certified and appreciated by experienced jewelers.
What Technologies Are Used For the Production of Lab Diamonds?

To "grow" laboratory diamonds, an environment is created where they develop naturally. It completely duplicates the conditions for the formation of diamonds in the bowels of the Earth at a depth of approximately 150 km.
Each lab-grown diamond is created from a tiny diamond crystal. Then, it is placed in a chamber that reproduces the natural process of carbon crystallization into a diamond.
Two methods are often used - High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT), or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Both of them recreate the natural environment for the development and growth of a diamond in nature.
High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT)
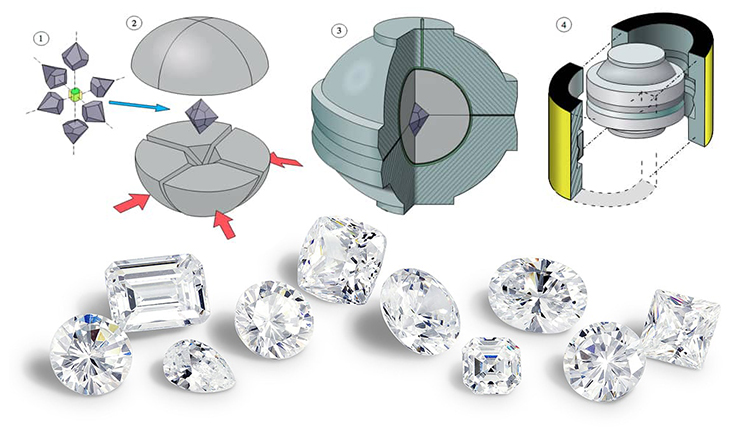
The HPHT method mimics the natural process but significantly speeds it up. A temperature of approximately 1,500 degrees Celsius is maintained to grow diamonds in special containers. In addition, the process is under high pressure of 50-70 thousand atmospheres.
Inside the container is a molten metal alloy consisting of iron, nickel, cobalt and other metals, and graphite. Finally, a substrate with small diamond crystals is placed in the container - a seed.
Further, an electric current is passed through the chamber, in which the metal serves as a catalyst for the crystallization of carbon on a seed - this is how precious stones grow. On the farm, one large diamond or several small ones grow in 12-13 days.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)

This technology irradiates hydrogen and methane gas with a thin layer of laboratory-grown diamond "seed" within a special chamber, where heat and pressure are introduced.
These carbon-rich gases are heated to a stage of active decay, forming layers of diamond seed. Finally, crystallization occurs under a carbon-saturated environment, and a solid diamond crystal is formed layer by layer.
Diamonds created using CVD technology have practically no foreign impurities, such as nitrogen or boron, giving them advantages even over natural diamonds for industrial and jewelry applications. Such diamonds are used to make beautiful jewelry that is not inferior to those with mined diamonds, although they are much cheaper.
Both methods are achievements of our century. Diamond growth has been significantly accelerated thanks to scientists and the latest technology.
What Is the Difference Between Lab and Natural Diamonds?

Laboratory diamonds have the same hardness, brilliance, and transparency as natural stones. They are cut and polished using the same equipment and methods as diamonds from the Earth.
The characteristics of natural and laboratory diamonds are identical. So the bottom line is that a diamond formed three billion years ago in the bowels of the Earth and a diamond grown in a laboratory are precisely the same.
Diamonds of different origins with similar characteristics look the same even to experienced eyes. However, microscopes or magnifiers cannot distinguish between lab-grown and mined diamonds.
Inexpensive diamond testing tools used by jewelers are only designed to determine if a diamond is fake or real. Furthermore, these tools are elementary and cannot distinguish between natural and lab-grown diamonds.
The gemological equipment needed to identify a mined or grown diamond reliably is quite expensive, costing more than $15,000, and not available to everyone. Thus, laboratory diamonds are identical to natural stones in all their characteristics, and the difference between them is only in origin.
How Are Lab Diamonds Classified?

Lab-grown diamonds are classified according to the same standards as mined diamonds and have certificates from international gemological laboratories with the required mark of origin (GIA, HRD, IGI, Moscow State University, MGL, and others).
According to the characteristics of laboratory diamonds, they are divided into:
• type Ia - colorless and near-colorless;
• type Ib - tinted;
• type IIa - colorless and near-colorless, which contain some nitrogen inclusions;
• type IIb - tinted, which contains some nitrogen inclusions;
• type IIIa - colorless and near-colorless;
• type IIIb - tinted, which contains tiny inclusions.
The highest quality diamonds are type Ia and type IIa. They are the most transparent, durable, and brilliant stones in great demand among jewelers.
Are Lab-Grown Diamonds More Sustainable and Ethical?

Indeed, the growing popularity of laboratory diamonds worldwide is mainly due to the fashion for responsible consumption. People refuse plastic and disposable bags, and natural fur coats have gone out of fashion. Therefore, it is natural that many are interested in ethical jewelry.
Lab-made diamonds offer consumers an ethical and affordable alternative. In addition, these have a much lower environmental impact than mined diamonds. Producing them does not require the extraction of minerals from deep pits, and they have a much smaller carbon footprint. It makes lab-grown diamonds the perfect choice for those who care about the environment and want to buy jewelry without ethical misgivings.
In addition, many believe that minerals absorb energy. A hard-earned diamond hardly carries good vibrations. You fill a diamond grown in a laboratory with positive energy. It will be a personal talisman with good energy.
Therefore, laboratory diamonds are sustainable and ethical since they involve no unethical practices and have a much lower environmental impact than mined diamonds.
The Future of Lab-Grown Diamonds

By 2030, the market for lab-grown diamonds is expected to grow to $49.9 billion. As a result, jewelry brands are actively introducing such stones into their collections, and their market share in the jewelry industry will only grow.
The consumer has an important influence on the jewelry market. However, today, millennials are changing the diamond industry, as members of this generation are making more financially conscious decisions regarding the purchase of diamonds, choosing more environmentally friendly methods of creating diamonds.
In addition, laboratory diamonds are becoming increasingly popular due to their affordability and availability. As a result, more and more people are switching to lab-grown stones when it comes to jewelry purchases. Consequently, the demand for laboratory diamonds is growing rapidly, and their share of the global diamond market is expected to rise!
Bottom Line

Laboratory diamonds have many advantages over natural stones. They are more affordable, eco-friendly, and available in any size or cut. Furthermore, they are ethically and sustainably sourced, making them an attractive choice for those who care about the environment.
With increasing consumer demand, the market for laboratory diamonds is expected to grow significantly over the next decade. Therefore, laboratory diamonds are here to stay and will only become more popular as time goes on. So what are you waiting for? Get your lab-grown diamond today!

Leave a Comment